Disponible uniquement en lange anglaise
The New Way in DR and AMD Supplementation
Using Ocufolin® forte as a supplement to reduce the risk of Diabetic Retinopathy (DR)
In a systematic review and meta analysis high homocysteine levels have been shown to be a risk factor for DR (Xu et al. 2014). The status of vitamins B was identified to be a major cofounding factor for DR (Satyanarayana et al. 2011). Patients with elevated homocysteine showed coincidently low folate and vitamin B12 levels (Fotiou et al. 2014). Above a threshold level for homocysteine of >13 μmol/l the risk of DR increases significantly.
Vitamin D is a multi functional fat soluble ingredient identified as a potent inhibitor of retinal neovascularization in ischemic retinopathy (Qin et al. 2017).
In response to these results, two ophthalmologists in the USA developed Ocufolin®, a formulation designed specifically for use in ophthalmology. It is currently the only ocular supplement containing the particularly active form of folic acid: L-Methylfolate Calcium.
An important criterion in developing the formulation of Ocufolin® was the description of the existence of the folate receptor alpha (FRα) and the reduced folate transporter (RFT-1) at the retinal pigment epithelium (RPE). This evidenced the important role of folate in retinal metabolism (Smith et al. 2000).
Riskfactor Homocysteine
Elevated Hcy levels along with oxidative stress have been associated in the etiology of several vascular diseases that can lead to the development of choroidal neovascularization (CNV) in AMD and DR (Singh et al. 2017, Huang et al. 2015). Hcy may be a potential useful biomarker in assessing the microvascular risk in diabetes, and hyperhomocysteinemia is a potential risk factor for DR, especially PDR (Xu et al. 2014). Hyperhomocysteinemia (HHcy) is associated with several human visual disorders, such as diabetic retinopathy (DR) and age-related macular degeneration (AMD). Breakdown of the blood-retinal barrier (BRB) is linked to vision loss in DR and AMD (Mohamed et al. 2017).
Correlation Homocysteine and Folate
Elevated serum tHcy and folate and vitamin B12 deficiencies predicted increased risk of incident AMD, which suggests a potential role for vitamin B12 and folate in reducing AMD risk (Gopinath et al. 2013, BMES).
Folic Acid versus L-Methylfolate
Naturally occurring 5-MTHF has important advantages over synthetic folic acid – it is well absorbed even when gastrointestinal pH is altered and its bioavailability is not affected by metabolic defects (Scaglione et al. 2013). Not only is L 5-MTHF more effective in raising blood folate concentrations after 12 weeks than folic acid, but it is also unlikely to mask vitamin B-12 deficiency (Henderson et al. 2018). Folic acid is a synthetic form of the vitamin, which is only found in fortified foods, supplements and pharmaceuticals. It lacks coenzyme activity and must be reduced to the metabolically active tetrahydrofolate form within the cell. (Pietrzik et al., 49, (2010), 535).
Nutrition versus Supplementation
Disease-induced nutritional deficiencies often cannot be addressed by nutrient intakes derived from a whole food-based diet alone (Stover et al. 2017).

Using Ocufolin® forte as a supplement to reduce the risk of Age-related Macular Degeneration (AMD)
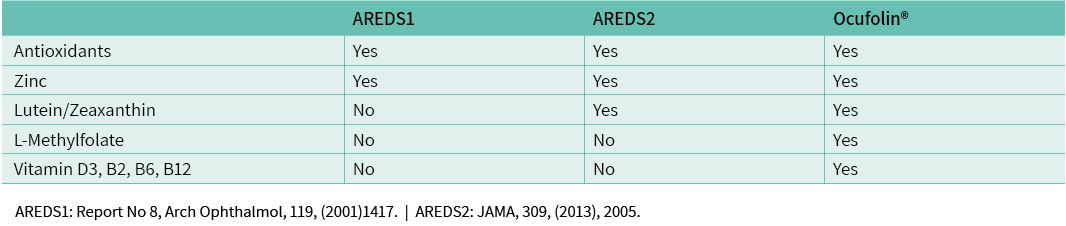
The ARED Studies showed reduced progression to advanced stages of the disease in AMD patients with morphological AMD impairment. However, the effect evidenced in the ARED Studies was restricted to the combination of antioxidants, zinc and Lutein/Zeaxanthin. After AREDS, efforts to develop appropriate formulations ceased. The impact of folates on the complex retinal pathology of AMD was hardly considered.
Folate deficiency has been identified as an important pathogenic factor in eye diseases such as AMD. Insufficient folate levels lead to increased homocysteine. Homocysteine levels >15 μmol/l are linked to increased risk of AMD incident in patients under 75. Additionally, hyperhomocysteinemia combined with low Vitamin B12 levels represents a major risk factor (Blue Mountains Eye Study, 2013).
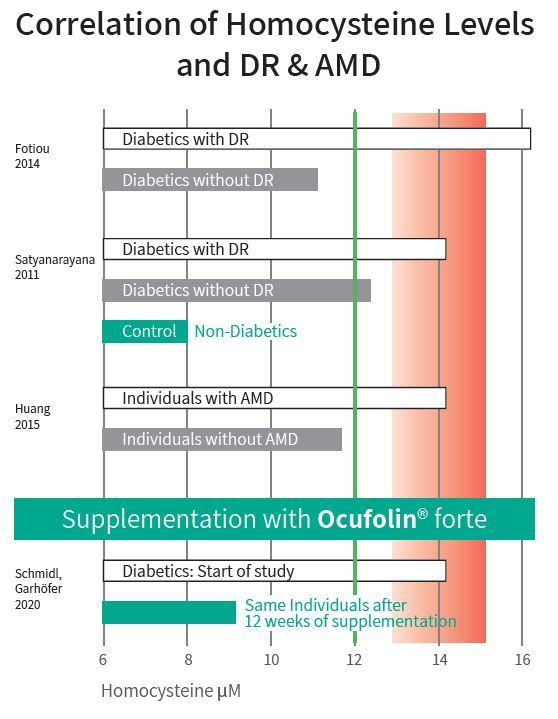
Fotiou 2014: Hc extremely elevated in 65 T2D-patients with DR compared to 75 T2D controls without DR.
Satyanarayana 2011: Hcy elevated in 200 Typ-2 Diabetes (T2D) patients with DR compared to 100 T2D-patients without DR.
Huang 2015: Hcy elevated in 1'072 AMD-cases compared to 1'202 controls, (Meta-Analysis of 11 studies).
Schmidl, Garhöfer 2020: Hcy-level efficiently reduced in 24 diabetic patients (T1DM, T2DM) with and without DR.
Using Ocufolin® forte as a supplement to reduce the risk of Diabetic Retinopathy (DR)
In a systematic review and meta analysis high homocysteine levels have been shown to be a risk factor for DR (Xu et al. 2014). The status of vitamins B was identified to be a major cofounding factor for DR (Satyanarayana et al. 2011). Patients with elevated homocysteine showed coincidently low folate and vitamin B12 levels (Fotiou et al. 2014). Above a threshold level for homocysteine of >13 μmol/l the risk of DR increases significantly.
Vitamin D is a multi functional fat soluble ingredient identified as a potent inhibitor of retinal neovascularization in ischemic retinopathy (Qin et al. 2017).
In response to these results, two ophthalmologists in the USA developed Ocufolin®, a formulation designed
specifically for use in ophthalmology. It is currently the only ocular supplement containing the particularly active form of folic acid: L-Methylfolate Calcium.
An important criterion in developing the formulation of Ocufolin® was the description of the existence of the folate receptor alpha (FRα) and the reduced folate transporter (RFT-1) at the retinal pigment epithelium (RPE). This evidenced the important role of folate in retinal metabolism (Smith et al. 2000).
Difference between folic acid and L-Methylfolate
Studies by the US ophthalmologists showed many of their patients had a genotype which inhibits the metabolism of folic acid to L-methylfolate (MTHFR polymorphism). For patients with this genotype, even increased intake of folic acid does not guarantee that the retina is supplied with sufficient metabolized active folate.
The New Way in DR and AMD Supplementation
Ocufolin®: State of the Art
Calcium L-Methylfolate, is a highly bioavailable and active ingredient. This is the new active agent in Ocufolin®. Using calcium-L-methylfolate in a supplement provides the retina with active folate to reduce or reverse deficiencies resulting from genetic, dietary causes or diseases.
- The AREDS1 formula (2001): the combination of antioxidants, β-carotene and zinc can reduce the progress to more advanced stages of AMD by 25 % over a period of 6.3 years.
- The AREDS2 formula (2013): patients with Lutein deficiency benefit most from Lutein/Zeaxanthin (25 % reduction in the likelihood of further deterioration, as in AREDS1 with β-carotene). Unsaturated fatty acids provided no additional benefit in the ARED Study.
- Ocufolin®-formula: the essential components are L-methylfolate, B-vitamins, vitamin D, NAC plus ingredients from the ARED2 Study galenically optimized.
Reduction Homocysteine (Effect or Dietary Supplements)
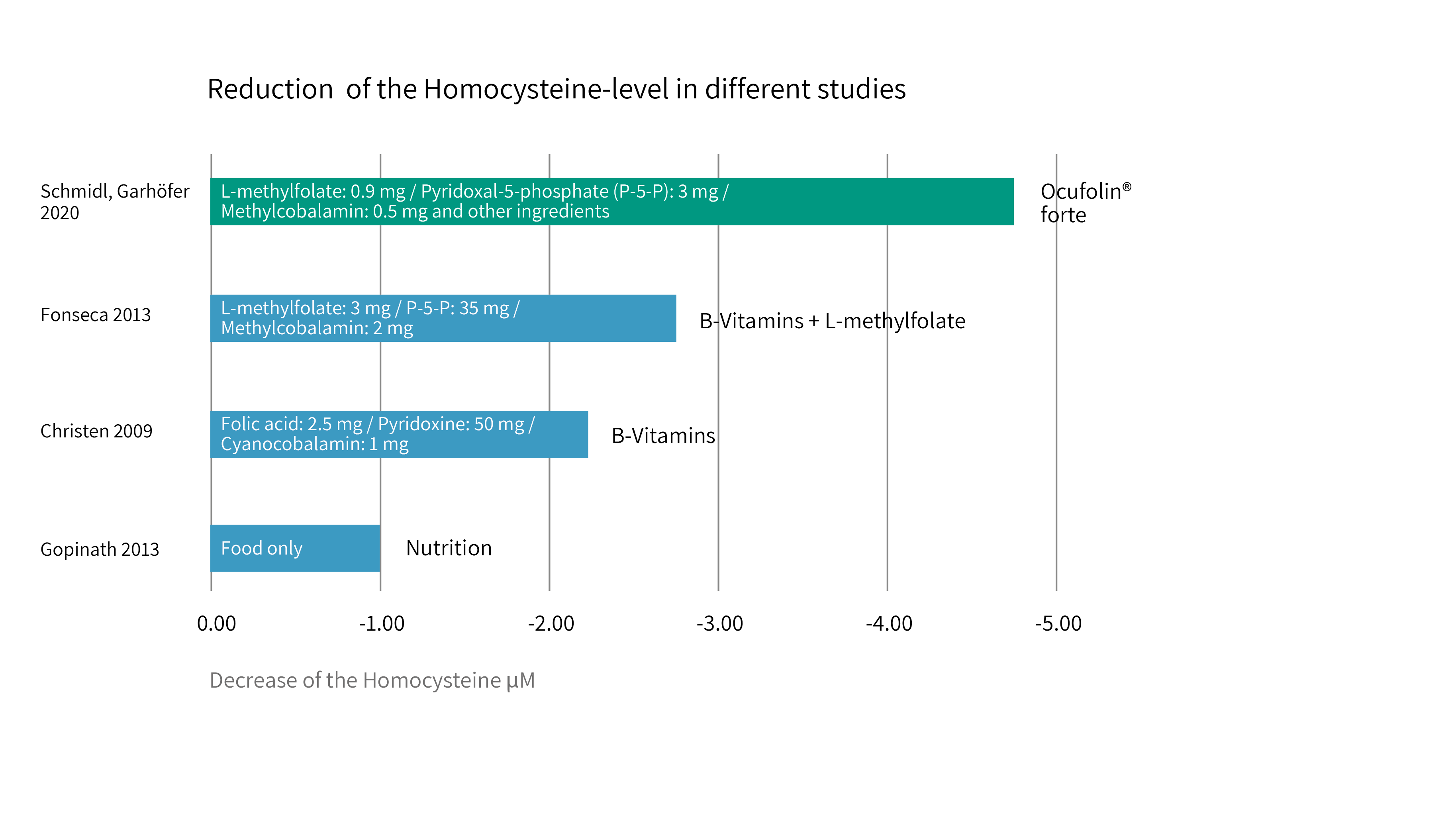
Schmidl, Garhöfer 2020, Mol. Vis., 26, (2020), 326: Hcy-level most efficiently reduced in DM patients after intake of Ocufolin® forte containing significantly lower quantities of each ingredient.
Fonseca et al., AM J Med, 126, (2013), 141: Hcy-level significantly reduced in T2D patients after intake of Metanx (T2D patients with peripheral neuropahty), "Medical Food"
Christen 2009: Hcy-level reduced in treated patients compared to placebo. AMD-incidents correlated with Hcy. (WAFACS)
Gopinath 2013: Hcy-level reduced in patients with intake of folate and B12 from food. (BMES)
Pilot Study Ocufolin® forte
At the University of Vienna a pilot study assessed the effect of a 3-month folate supplementation with Ocufolin® forte on systemic homocysteine plasma concentration and ocular blood flow in patients with diabetes. Results show that 3 months intake of Ocufolin® forte is capable of significantly reducing blood homocysteine level in patients with diabetes. In addition, a tendency towards an increase in total retinal blood flow was observed. In diabetic retinopathy, it has been shown that the disease is associated with early retinal vascular dysregulation. “In the later states of the disease, retinal tissue hypoxia is a major trigger of sight-threatening neovascularization. In age-related macular degeneration, there is increasing evidence that reduced blood flow in the choroid is associated with the development and progression of the disease” (Pemp. Schmetterer, Can J Ophthalmol, 43, (2008), 295).
In case studies improvements in diabetic and hyper-tensive retinopathy have been reported (Wang et al., Eye and Vision, 2019; 6:21).
Availability of Ocufolin®
Ocufolin® is presented in Blister Packs with 90 Capsules, in two formulations, Ocufolin® forte and Ocufolin® prevent.
In Europe, it has to date already been registered and has been available in Austria, Switzerland and Germany as a supplement since June 2016. Additional European Countries to follow in the near future. Ocufolin® is recommended to be used under the supervision of an ophthalmologist.
Importance of Formulation
Ocufolin® in its lipophilic galenic preparation ensures proper absorption.
Encapsulating or solubilizing the ingredient in lipid excipients can lead to increased solubilization and absorption, resulting in enhanced bioavailability. (Kalepu et al., Acta Pharmaceutica Sinica B, 2013; 3(6): 361–372).
The importance of “nutritional and medical food therapies for diabetic retinopathy” has been re-viewed (Shi et al., Eye and Vision, 2020; 7:33)
Composition in Metabolic Cycles
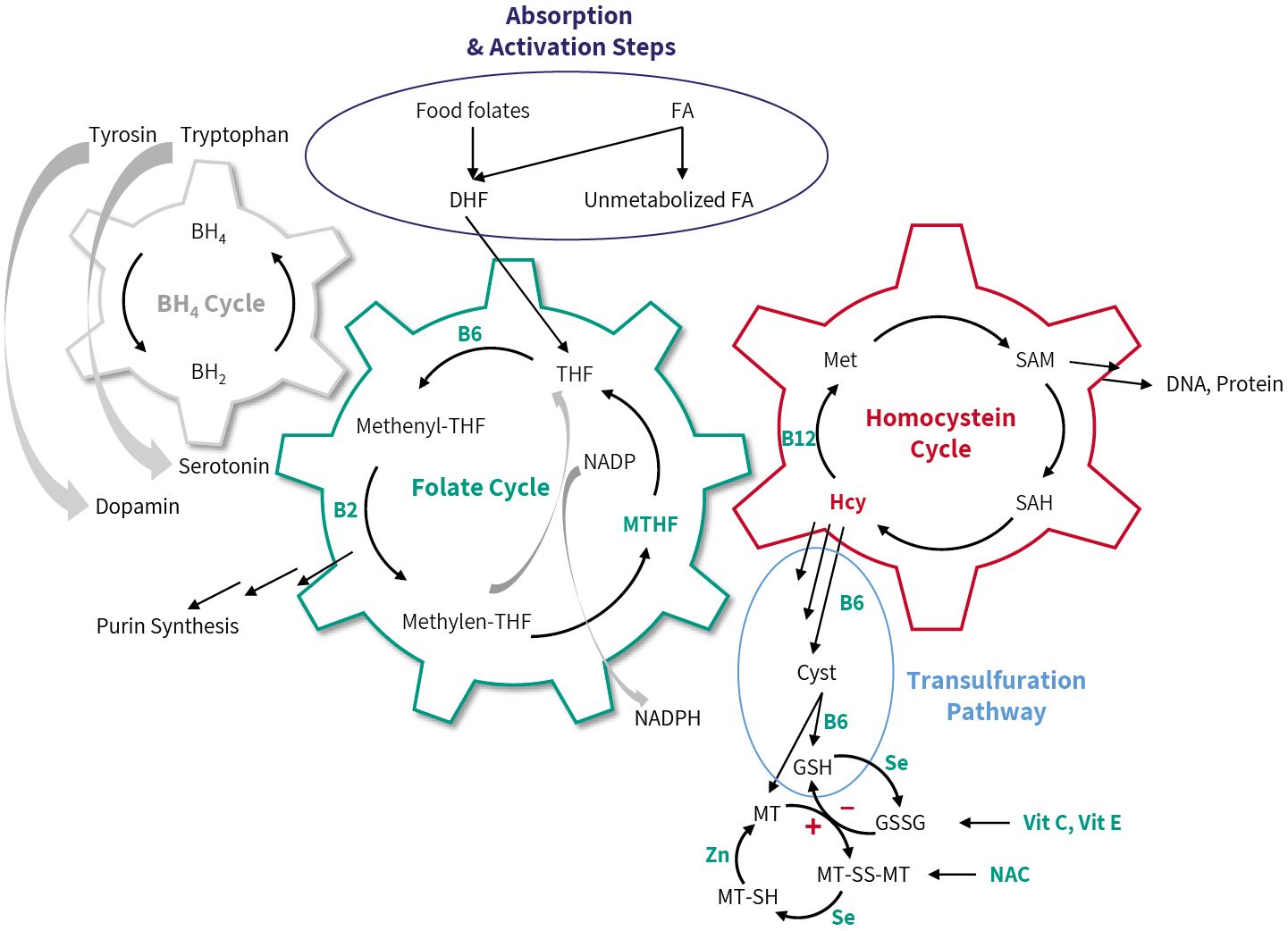
Sources: Lee et al., J Clin Org, 127, (2017), 1856; Ruttkay-Nedecky et al., Int J Mol Sci, 14 (2013), 6044; Dahlhoff et al., PLOS One, 8 (2013), e57387; Schmidt et al., Clin Sci, 113, (2007), 47; Ueland et al., Ann. Rev. Nutr. 35, (2015), 33; Fan et al., Nature, 510, (2014), 298; Fernandez-Arroyo et al., Oncoscience, 2, (2016), 958.
 Français
Français  Deutsch
Deutsch  English
English  Italiano
Italiano  Español
Español